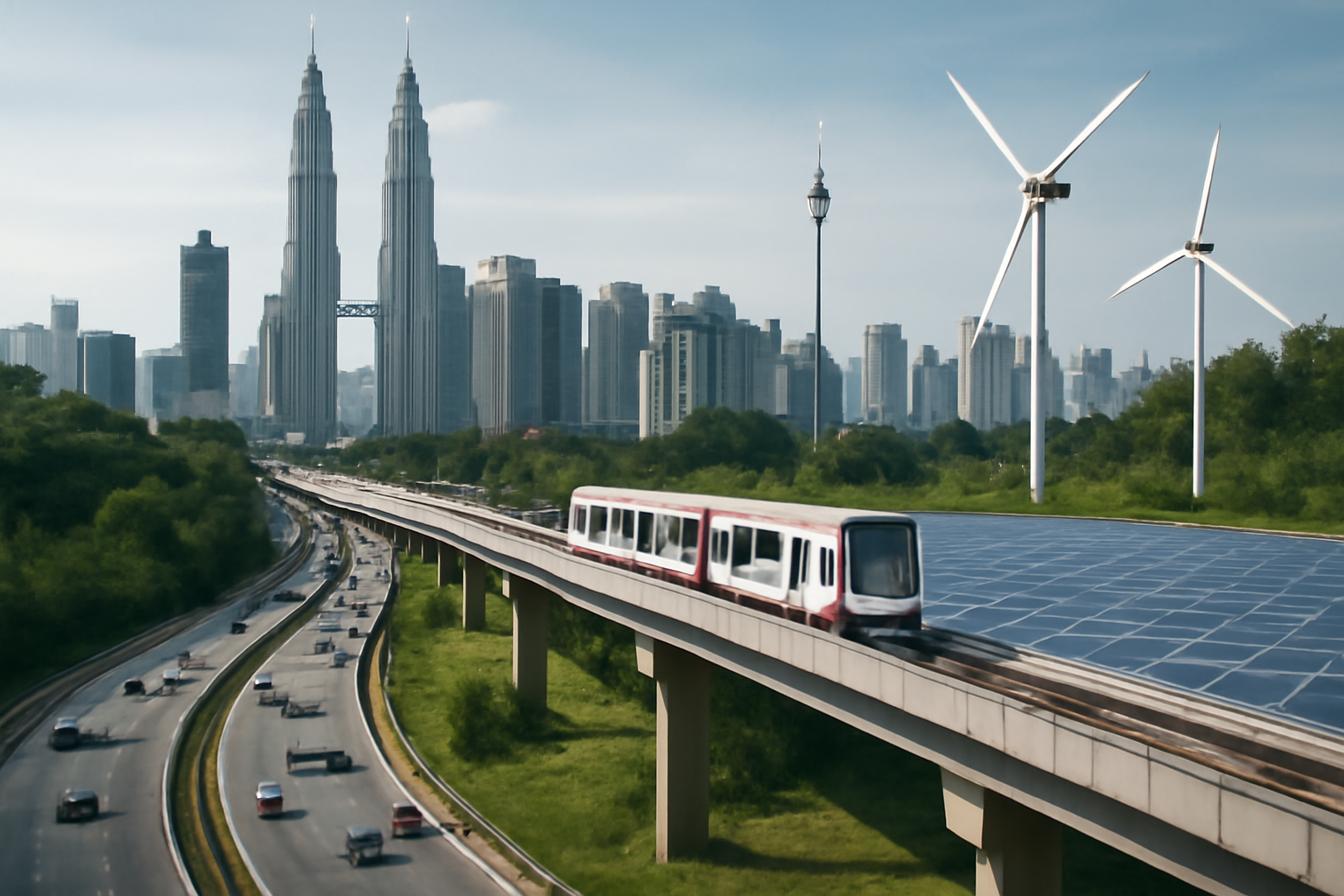
Infrastructure development in Malaysia plays a pivotal role in connecting its various regions and enhancing its long-term economic and social prospects. The country’s strategic infrastructure investments are designed not only to link urban and rural areas but also to position Malaysia as a global leader in trade, innovation, and sustainability.
Improving Regional Connectivity
Malaysia’s extensive infrastructure network is essential for linking its diverse regions, including both the Peninsula and Borneo. Major highways like the North-South Expressway and the Pan-Borneo Highway are vital for improving regional connectivity. These road systems facilitate the free flow of goods and services, enhancing trade and reducing logistical costs across the country.
Moreover, Malaysia’s focus on upgrading its rail and air transportation networks further strengthens its position as a transport hub in Southeast Asia. High-speed rail links, such as the proposed Kuala Lumpur-Singapore High-Speed Rail, promise to revolutionize travel and business operations between the two nations.
Economic Impact of Infrastructure Development
Infrastructure investment is a major driver of Malaysia’s economic development. Improved connectivity stimulates business activity, attracts foreign investment, and boosts productivity across various sectors. By investing in infrastructure, Malaysia can attract multinational companies, particularly in industries like electronics, automotive, and agriculture.
In recent years, digital infrastructure has also become a priority. The expansion of high-speed internet networks and the introduction of 5G technology are expected to fuel Malaysia’s transformation into a digital economy, driving innovation, entrepreneurship, and competitiveness.
Sustainability in Infrastructure Growth
Malaysia is committed to developing sustainable infrastructure that promotes environmental stewardship. Green building practices, renewable energy solutions, and the promotion of public transportation systems are all part of the country’s broader plan to create a low-carbon economy. These sustainable projects not only reduce the nation’s ecological footprint but also improve the overall quality of life for its citizens.